
Sports concussion (diagnosis and assessment of recovery)Īetna considers the BrainScope One system (Ahead 300) for evaluation of concussion / traumatic brain injury experimental and investigational because of insufficient evidence. Sepsis-associated encephalopathy prognosis. Predicting response to psychotropic medication. Prediction of outcomes in children following cardiac arrest. Minimally conscious state/persistent vegetative state. Depressed mood after stroke (screening). Chronic pain (diagnosis and guide to strategies for pain control). Attention disorders (including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder). Asperger syndrome and other autism spectrum disorders. In accordance with the American Academy of Neurology/American Clinical Neurophysiology Society's assessment and available evidence, Aetna considers the use of quantitative EEG experimental and investigational for all other indications, including any of the following diagnoses because there is inadequate scientific evidence to prove its clinical usefulness for these indications: For topographic voltage and dipole analysis in pre-surgical evaluations for intractable epilepsy. For screening for possible epileptic spikes or seizures in long-term EEG monitoring or. For screening for possible epileptic seizures in high-risk ICU members or. For evaluation of dementia and encephalopathy when the diagnosis remains unresolved after initial clinical evaluation or. For evaluation of certain members with symptoms of cerebrovascular disease whose neuroimaging and routine EEG studies are not conclusive or. For continuous EEG monitoring by frequency-trending to detect early, acute intracranial complications in the operating room or intensive care unit (ICU) or. For ambulatory recording of EEG to facilitate subsequent expert visual EEG interpretation or. However, if you have a sleep-related problem, the test may last for several hours while a person sleeps.Aetna considers the use of quantitative EEG (brain mapping), also known as BEAM (Brain Electrical Activity Mapping), medically necessary only as an adjunct to traditional EEG for any of the following: Common sleep problems include sleep apnea, insomnia, or restless leg syndrome. A stroke is when the blood supply to your brain is cut off or reduced, causing symptoms such as trouble walking, talking, or a drooping face. Inflammation of the brain (encephalitis). These can include concussion or traumatic brain injury. This is when a person has one or more seizures and they don’t go away over time. Seizures.This is when certain brains cells (neurons) send uncontrolled messages over and over again. The test will also help the doctor diagnose neurological problems.Īn EEG is commonly used to diagnose the following conditions: The EEG helps the doctor look at these messages and see if they are working well. 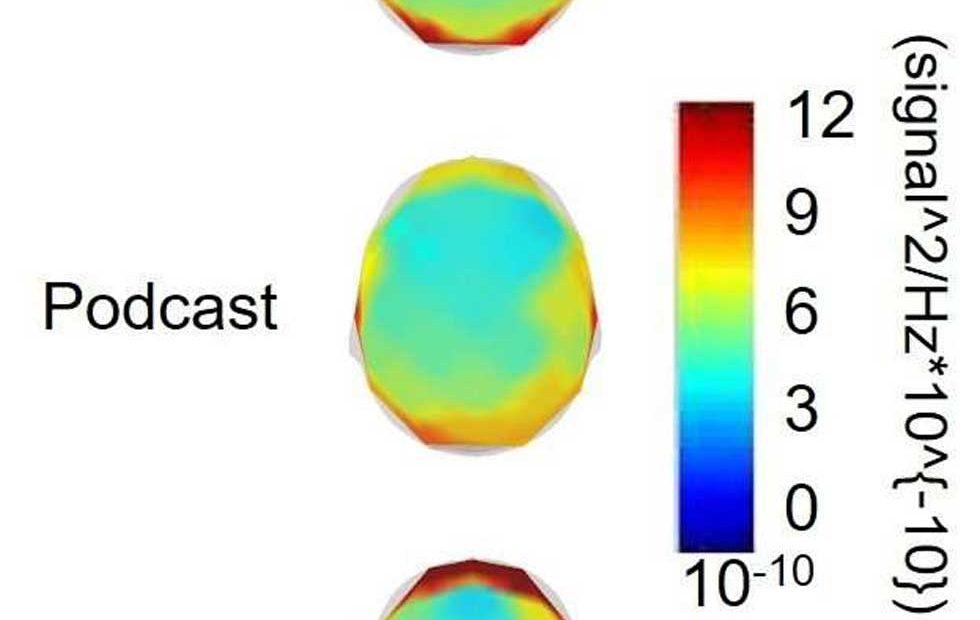
The brain’s electrical messages also control thinking and memory. This information is sent back and forth from the brain to the body with small electrical messages.
The brain also sends information to all parts of the body to control breathing, or how fast the heart beats, etc.
#Brain eeg skin
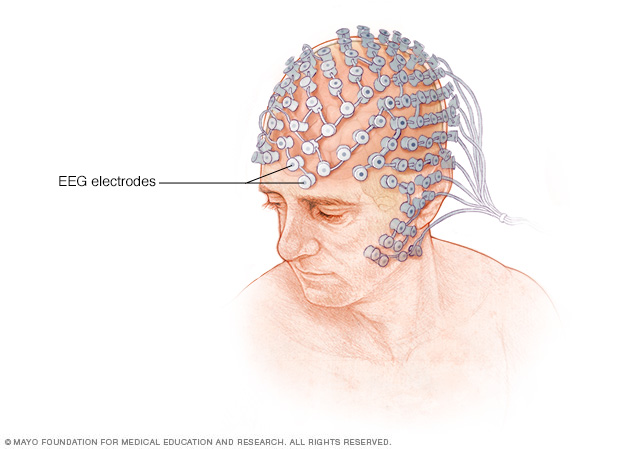
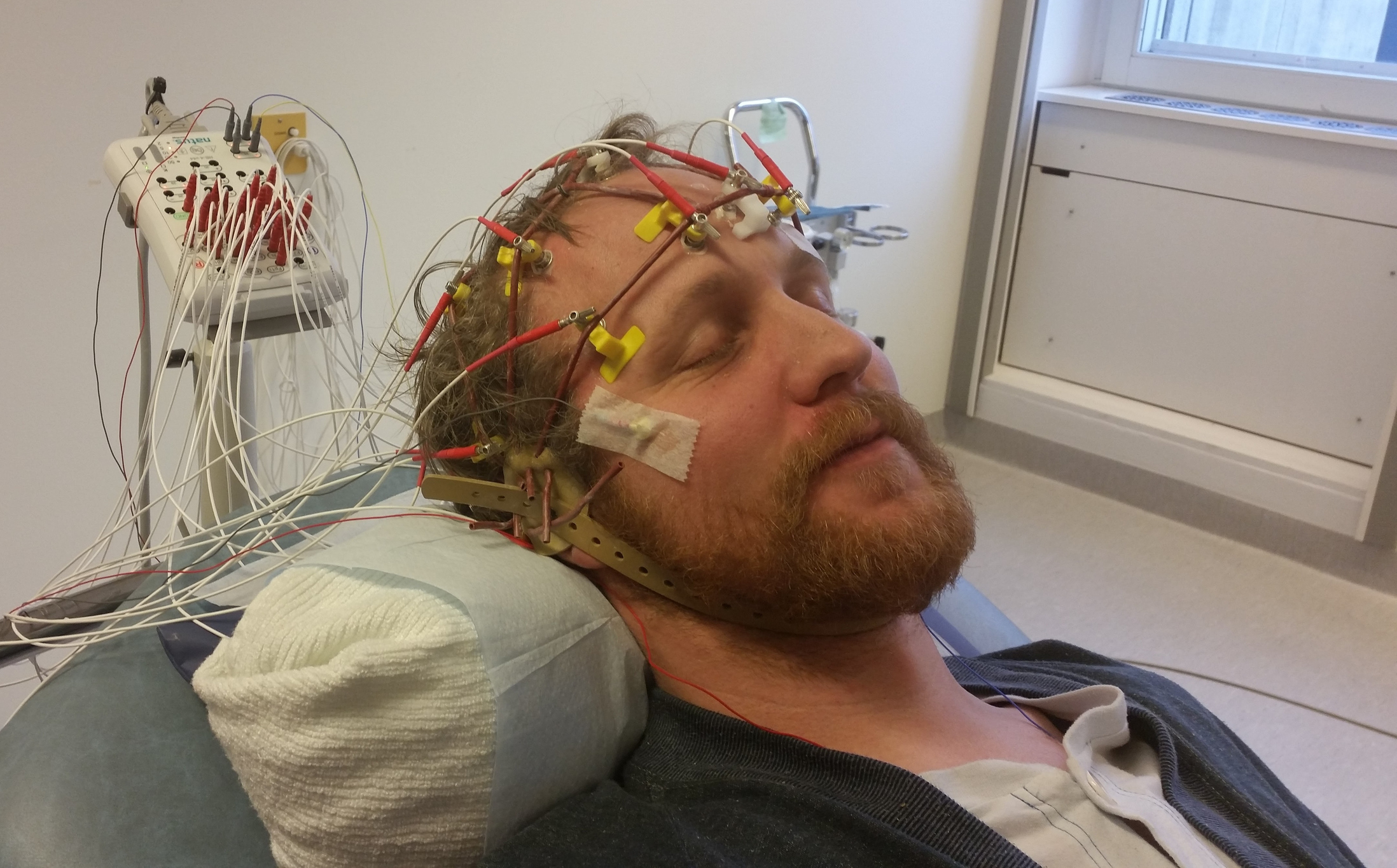
For example, the brain gets information from the eye about light, from the ears about sound, and from the skin about the sensation of touch. The brain gets information from all parts of the body. A doctor can look at the results from the EEG and get information on how the brain is working. The electrodes can detect electrical signals between the cells in the brain.

During the test, small electrodes (small metal discs) are placed on the head. An EEG, or electroencephalogram, is a recording of the electrical activity of the brain.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
